Table of Contents
ToggleA brief history of British Airways
British Airways (BA) has a storied history dating back to the early days of aviation. Its roots can be traced to the birth of civil aviation in the United Kingdom.
Early Beginnings (1919-1974): The origins of British Airways can be found in the establishment of several airlines that eventually merged to form the modern-day carrier. One of its earliest predecessors, Aircraft Transport and Travel Limited (AT&T), began operations in 1919, offering the world’s first daily international scheduled air service between London and Paris. Over the following decades, various airlines emerged, including Imperial Airways and British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC), which operated long-haul routes connecting the UK with its colonies and other international destinations.
Formation of British Airways (1974): In 1974, the British government enacted the Civil Aviation Act, which led to the merger of BOAC and British European Airways (BEA) to form British Airways (BA). This merger was aimed at consolidating the UK’s airline industry and creating a single national carrier to compete more effectively in the increasingly competitive global aviation market.
Privatization and Expansion (1980s-1990s): During the 1980s, British Airways underwent significant changes under the leadership of CEO Lord King. The airline was privatized in 1987, leading to increased efficiency and a focus on profitability. British Airways expanded its route network, introduced new aircraft, and invested in modernizing its fleet and services. The airline became known for its premium service offerings and innovative marketing campaigns, such as the iconic “World’s Favorite Airline” slogan.
Global Expansion and Alliances (2000s-Present): In the early 2000s, British Airways faced challenges due to increased competition from low-cost carriers and the effects of global economic downturns. However, the airline adapted by forming strategic alliances with other carriers and expanding its network through code-share agreements and joint ventures. In 2011, British Airways merged with Spain’s Iberia to create International Airlines Group (IAG), further strengthening its position in the global market.
Adapting to Challenges (2010s-Present): In recent years, British Airways has faced various challenges, including rising fuel costs, labor disputes, and the impact of events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite these challenges, the airline has continued to innovate and invest in its fleet, services, and technology. It has also focused on sustainability initiatives and enhancing the customer experience through improvements in onboard amenities and digital services.
Who Owns British Airways
British Airways is owned by International Airlines Group (IAG), a multinational airline holding company headquartered in London, England.
British Airways Mission Statement
British Airways’ mission is to connect people, places, and cultures across the globe, providing customers with exceptional service and creating memorable travel experiences.

How British Airways makes money
British Airways generates revenue through various streams, primarily focusing on passenger travel, cargo services, and ancillary offerings. Ticket sales form the backbone of its income, catering to diverse customer segments ranging from business travelers to vacationers.
Additionally, British Airways capitalizes on its extensive route network, offering flights to numerous destinations worldwide, each contributing to its revenue through ticket sales. Beyond passenger travel, British Airways operates a robust cargo service, transporting goods and merchandise across its global network. Ancillary services also play a significant role, with offerings such as onboard dining, seat upgrades, and travel insurance contributing additional revenue.
Moreover, British Airways leverages partnerships and alliances with other airlines to expand its reach and offer joint services, further bolstering its revenue streams. Overall, British Airways’ multi-faceted approach to revenue generation ensures a steady income flow while catering to the diverse needs of its customers and partners in the aviation industry.
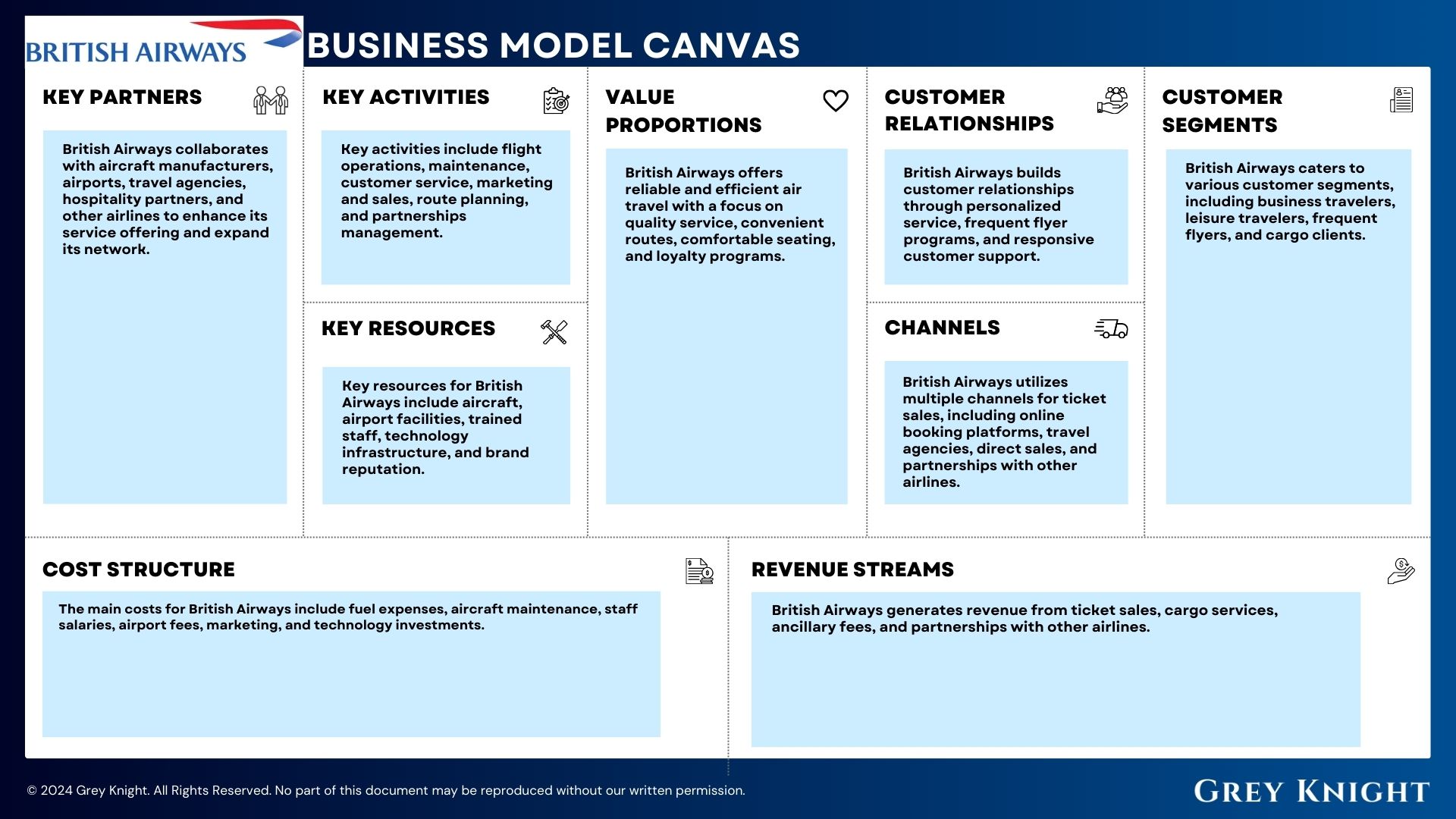
British Airways Business Model Canvas:
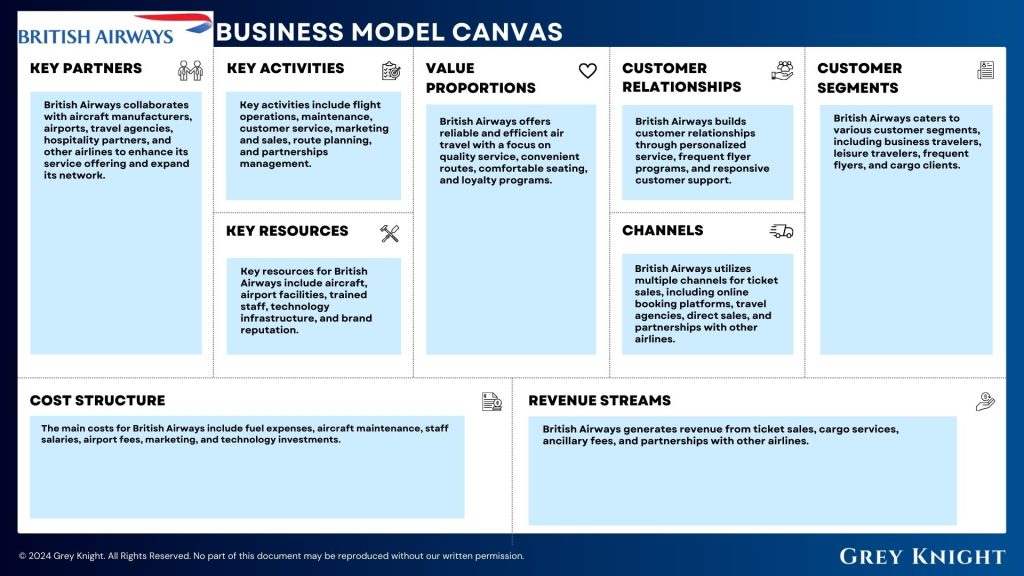
- Customer Segments: British Airways caters to various customer segments, including business travelers, leisure travelers, frequent flyers, and cargo clients.
- Value Propositions: British Airways offers reliable and efficient air travel with a focus on quality service, convenient routes, comfortable seating, and loyalty programs.
- Channels: British Airways utilizes multiple channels for ticket sales, including online booking platforms, travel agencies, direct sales, and partnerships with other airlines.
- Customer Relationships: British Airways builds customer relationships through personalized service, frequent flyer programs, and responsive customer support.
- Revenue Streams: British Airways generates revenue from ticket sales, cargo services, ancillary fees, and partnerships with other airlines.
- Key Resources: Key resources for British Airways include aircraft, airport facilities, trained staff, technology infrastructure, and brand reputation.
- Key Activities: Key activities include flight operations, maintenance, customer service, marketing and sales, route planning, and partnerships management.
- Key Partners: British Airways collaborates with aircraft manufacturers, airports, travel agencies, hospitality partners, and other airlines to enhance its service offering and expand its network.
- Cost Structure: The main costs for British Airways include fuel expenses, aircraft maintenance, staff salaries, airport fees, marketing, and technology investments.
British Airways’ Competitors
British Airways faces competition from other global airlines such as Lufthansa, Air France-KLM, Emirates, and Delta Air Lines, among others.
British Airways’ SWOT Analysis

Strengths
- Strong Brand Recognition: British Airways enjoys high brand awareness globally, synonymous with quality service and reliability.
- Extensive Route Network: The airline operates a vast network of routes, connecting major cities and destinations worldwide, offering passengers a wide range of travel options.
- Premium Service Offerings: British Airways is known for its premium cabin experience, including luxurious amenities, comfortable seating, and exceptional customer service.
- Membership in Global Alliances: Being a part of the oneworld alliance provides British Airways with access to a larger customer base, seamless connections, and reciprocal benefits with partner airlines.
- Technological Innovation: British Airways invests in cutting-edge technology to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experience, and stay ahead in the competitive aviation industry.
Weaknesses
- Vulnerability to Economic Factors: Fluctuations in fuel prices, currency exchange rates, and economic downturns can impact British Airways’ profitability and operational costs.
- High Operating Costs: Maintaining a large fleet of aircraft, along with expenses related to airport fees, maintenance, and staff salaries, contributes to British Airways’ high operating costs.
- Dependence on Hub Operations: British Airways heavily relies on its hub at London Heathrow Airport, which can pose challenges during capacity constraints, disruptions, or regulatory issues.
- Legacy Systems: Legacy IT systems and processes may hinder British Airways’ agility and ability to adapt quickly to changing market demands and technological advancements.
- Occasional Labor Disputes: Strikes or labor disputes with employees, including pilots, cabin crew, or ground staff, can disrupt operations and damage the airline’s reputation.
Opportunities
- Growth in Emerging Markets: Expanding routes and services to emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and South America presents opportunities for British Airways to tap into growing demand for air travel.
- Expansion of Premium Services: British Airways can further enhance its premium offerings, including first-class and business-class services, to attract high-yield travelers and increase revenue per passenger.
- Sustainable Aviation Initiatives: Investing in sustainable aviation practices, such as alternative fuels and carbon offset programs, aligns with growing environmental concerns and consumer preferences.
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging digital technologies and data analytics can improve operational efficiency, personalize customer experiences, and drive ancillary revenue opportunities for British Airways.
- Strategic Partnerships and Joint Ventures: Forming strategic partnerships or joint ventures with other airlines or travel providers can expand British Airways’ network, increase market share, and unlock new revenue streams.
Threats
- Intense Competition: British Airways faces fierce competition from other global airlines, low-cost carriers, and emerging competitors, which may pressure pricing and erode market share.
- Economic Uncertainty: Economic recessions, geopolitical tensions, or global events such as pandemics or natural disasters can impact travel demand and disrupt British Airways’ operations and financial performance.
- Regulatory Challenges: Changes in aviation regulations, taxation, or government policies, particularly related to Brexit or international trade agreements, may introduce complexities and compliance costs for British Airways.
- Security Concerns: Threats posed by terrorism, cybersecurity breaches, or safety incidents can undermine passenger confidence, disrupt operations, and lead to increased security measures and costs for British Airways.
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent environmental regulations, including emissions standards and carbon pricing mechanisms, may increase operating costs and require British Airways to invest in eco-friendly technologies and practices to remain compliant and competitive.
Concluding Analysis
What stands out most is how British Airways has weathered numerous storms over the decades. From economic downturns to technological revolutions, and most recently, the unprecedented challenges brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic, BA has consistently demonstrated its ability to navigate rough skies.
One of the key takeaways is British Airways’ knack for strategic evolution. Whether it was through mergers and acquisitions, privatization, or forging alliances with other carriers, BA has always been proactive in shaping its destiny. This agility has enabled the airline to expand its reach, enhance its service offerings, and stay ahead of the competition. Of course, no discussion of British Airways would be complete without mentioning its unwavering commitment to quality service and innovation. From introducing groundbreaking marketing campaigns to investing in state-of-the-art aircraft and passenger amenities, BA has continuously raised the bar for the aviation industry.
Looking ahead, British Airways faces a new set of challenges and opportunities. As the world emerges from the pandemic, the airline must navigate an uncertain economic landscape while also addressing growing concerns around sustainability and environmental responsibility. However, if history is any indication, British Airways is more than up to the task.
Additional Resources
To keep learning and advancing your career, we highly recommend these additional resources:
Business Model Canvas of The Top 1,000 Largest Companies by Market Cap in 2024
A List of 1000 Venture Capital Firms & Investors with LinkedIn Profiles
Peter Thiel and the 16 Unicorns: The Legacy of Thiel Fellowship