Table of Contents
ToggleA brief history of Sephora
Sephora, the renowned beauty retailer, has revolutionized the makeup industry, changing the way Americans shop for luxury cosmetics. With its roots in a small perfume shop in Limoges, France, Sephora has grown to become a dominant force in the global personal care and beauty product industry. This article explores the business practices and strategies that have propelled Sephora to its industry-leading position.
Sephora’s Assisted Self-Service Model
In a time when the cosmetics market relied heavily on service-based retail, Sephora introduced an innovative concept. Unlike traditional retailers where sales representatives worked behind glass counters, Sephora adopted an assisted self-service model. Customers were encouraged to freely test products in-store, creating an engaging and personalized shopping experience. With a dedicated station to try on lipsticks and eyeshadows, Sephora became a playground for makeup enthusiasts seeking to transform their looks. Despite the freedom to explore independently, customers could still rely on Sephora’s beauty advisors, brand-agnostic sales associates who offered trustworthy recommendations.
Disruptive Product Display
Sephora challenged the conventional way of displaying products by grouping makeup items from various brands together. Unlike fragrances and skincare products, which were traditionally separated by brand, Sephora arranged makeup items side by side. This unconventional approach allowed customers to compare and contrast products easily, fostering a sense of discovery and exploration.
Acquisition by LVMH
In 1997, Sephora was acquired by LVMH, a luxury retail conglomerate. This partnership provided Sephora with the advantage of promptly capitalizing on emerging trends. Many of the brands available in Sephora stores are owned by LVMH, including the popular Fenty Beauty by Rihanna. The exclusivity of these brands, combined with Sephora’s expansive reach, has contributed significantly to the retailer’s success.
Sephora’s Exclusive Product Line
Sephora’s influence over makeup brands stems from its position as an attractive platform for product sales. As a highly sought-after store, Sephora holds significant leverage in its relationships with beauty brands. This has led to the creation of Sephora’s own exclusive product line, further increasing its appeal and solidifying its loyal customer base.
Who Owns Sephora
Sephora is owned by LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, a French multinational luxury goods conglomerate.
Sephora’s Mission Statement

Sephora’s mission is to inspire clients to play in a world of beauty, while providing the best selection of brands and products.
How Sephora makes money
Sephora generates revenue primarily through the sale of beauty products, including cosmetics, skincare, haircare, fragrance, and beauty tools. Additionally, Sephora offers beauty services such as makeup application, skincare consultations, and beauty classes, contributing to its revenue stream.
Sephora’s Business Model Canvas
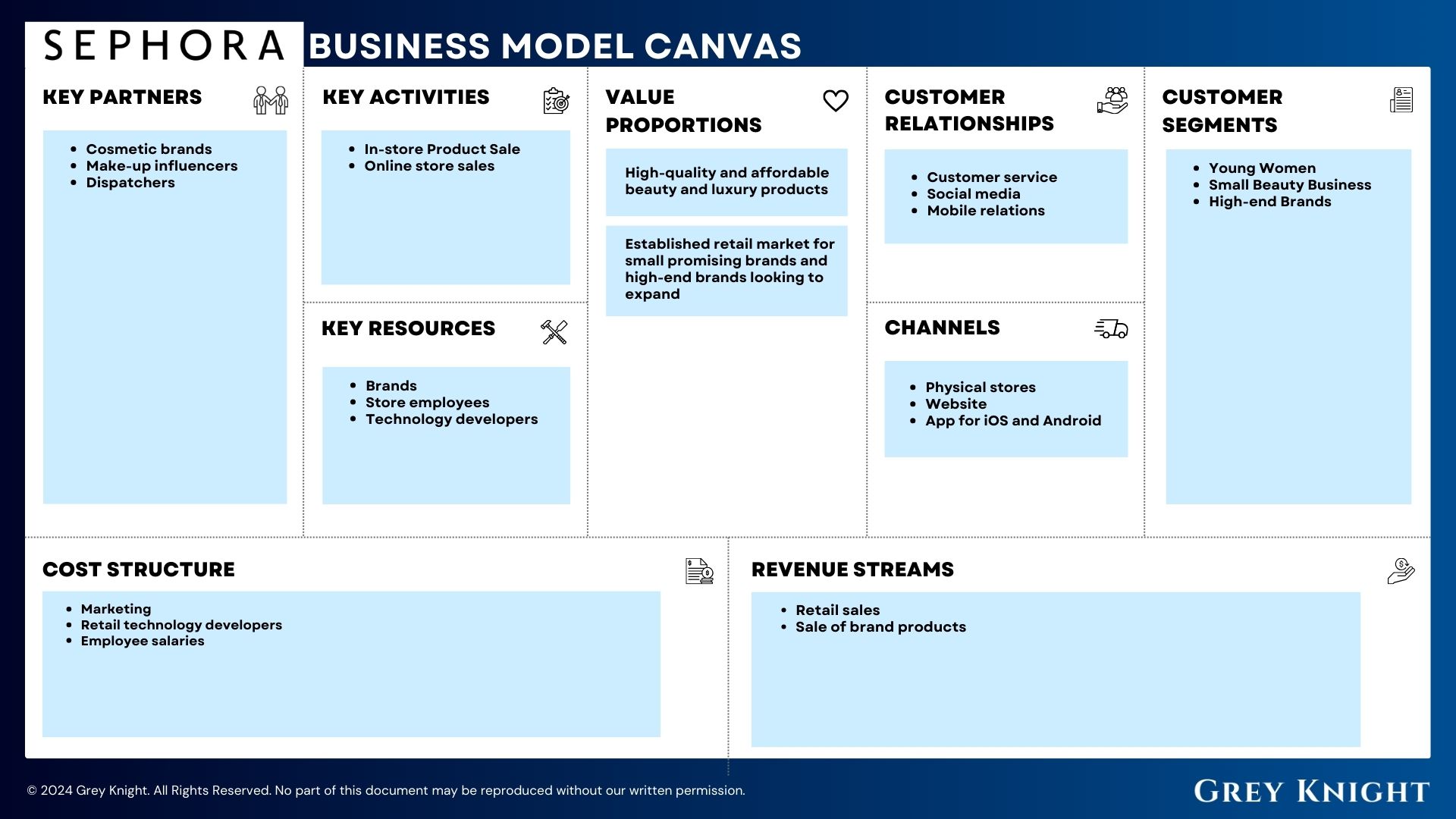
Customer Segments
- Beauty enthusiasts
- Makeup artists
- Skincare enthusiasts
- Fragrance enthusiasts
- Gift shoppers
Value Propositions
- Extensive range of beauty products from various brands
- Expert advice and consultations from beauty professionals
- In-store experiences and services
- Loyalty program with rewards and exclusive offers
Channels
- Brick-and-mortar stores
- E-commerce website
- Mobile app
Customer Relationships
- Personalized customer service in-store and online
- Loyalty program to foster long-term relationships
- Social media engagement and community building
Revenue Streams
- Sales of beauty products
- Beauty services fees
- Subscription services (e.g., Sephora Play beauty box)
Key Resources
- Physical store locations
- E-commerce platform
- Inventory management system
- Beauty experts and staff
Key Activities
- Merchandising and product selection
- Marketing and advertising campaigns
- Training staff on product knowledge and customer service
- Providing beauty services and experiences
Key Partners
- Beauty brands and suppliers
- Marketing agencies
- Payment processors
- Logistics and shipping partners
Cost Structure
- Cost of goods sold
- Rent and operational expenses for physical stores
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Employee salaries and benefits
- Technology infrastructure costs
Competitors
- Ulta Beauty
- Beauty retailers within department stores (e.g., Macy’s, Nordstrom)
- Online beauty retailers (e.g., Beautylish, Dermstore)
SWOT Analysis

Strengths
- Strong Brand Identity: Sephora has built a robust brand image synonymous with quality, variety, and innovation in the beauty industry. Its brand is trusted by consumers worldwide.
- Wide Product Range: Sephora offers an extensive selection of beauty products, including cosmetics, skincare, haircare, fragrances, and accessories. This variety caters to diverse consumer preferences and ensures a broad customer base.
- Exclusive Partnerships: The company collaborates with numerous high-end and niche beauty brands, offering exclusive product lines and limited-edition collections. These partnerships enhance Sephora’s appeal and differentiate it from competitors.
- Omnichannel Presence: Sephora has a strong omnichannel presence, integrating its online platform with brick-and-mortar stores. This seamless integration provides customers with convenience and accessibility, facilitating a personalized shopping experience.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Sephora’s Beauty Insider program incentivizes customer loyalty through rewards, discounts, and exclusive access to promotions. This program enhances customer retention and encourages repeat purchases.
Weaknesses
- High Price Points: Sephora’s products often come with premium price tags, which may deter budget-conscious consumers. Price sensitivity could pose a challenge, particularly during economic downturns or in markets with strong competition from lower-priced alternatives.
- Overwhelming Store Layout: Sephora’s stores can be overwhelming due to the sheer volume of products and the layout, which may make it challenging for customers to navigate and find specific items without assistance.
- Limited Focus on Sustainability: While Sephora has taken steps to promote sustainable beauty products and practices, its efforts in this area may not be as comprehensive compared to some competitors. A stronger emphasis on sustainability could enhance its appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
- Regional Variations: Sephora’s product offerings and marketing strategies may not always resonate equally well across different regions and cultures. Adapting to local preferences and cultural nuances can be a challenge, particularly in international markets.
- Dependence on Third-Party Brands: Sephora’s business model heavily relies on partnerships with third-party beauty brands. While this allows for a diverse product range, it also means that Sephora has limited control over product availability, pricing, and promotional activities.
Opportunities
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Sephora can capitalize on the growing demand for beauty products in emerging markets by expanding its presence in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East. These markets offer significant growth opportunities due to rising disposable incomes and changing consumer lifestyles.
- Digital Innovation: Investing in digital technologies and e-commerce platforms can enhance Sephora’s online shopping experience, enabling features such as virtual try-on tools, personalized recommendations, and augmented reality beauty tutorials. Embracing digital innovation can attract tech-savvy consumers and drive online sales.
- Diversification of Offerings: Sephora could explore diversifying its product offerings beyond traditional beauty products into adjacent categories such as wellness, skincare devices, or beauty tech gadgets. This expansion can cater to evolving consumer preferences and tap into new revenue streams.
- Focus on Inclusivity: With increasing demand for diversity and inclusivity in the beauty industry, Sephora can differentiate itself by championing inclusivity in its product range, marketing campaigns, and store experiences. Embracing diversity can resonate with a broader customer base and strengthen brand loyalty.
- Subscription Services: Introducing subscription-based services, such as beauty boxes or curated product bundles, can provide recurring revenue streams and deepen customer engagement. These services can offer convenience and personalized experiences, fostering long-term customer relationships.
Threats
- Competition from Retail Giants: Sephora faces competition from retail giants such as Ulta Beauty, Amazon, and department stores with dedicated beauty sections. Intense competition could pressure margins and market share, particularly as competitors expand their beauty offerings and invest in online channels.
- Counterfeit Products: The beauty industry is plagued by counterfeit products, which pose a threat to Sephora’s reputation and consumer trust. Ensuring product authenticity and implementing stringent anti-counterfeiting measures are critical to safeguarding the brand’s integrity.
- Shifts in Consumer Preferences: Changes in consumer preferences, such as a preference for clean beauty products, natural ingredients, or cruelty-free formulations, can impact Sephora’s product offerings and market positioning. Adapting to evolving trends while maintaining brand relevance is essential to staying competitive.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Sephora’s supply chain is vulnerable to disruptions, including raw material shortages, transportation delays, and geopolitical tensions. Any disruptions in the supply chain can lead to product shortages, impacting sales and customer satisfaction.
- Regulatory Challenges: Compliance with regulations governing the beauty industry, including product safety standards, labeling requirements, and marketing restrictions, presents ongoing challenges for Sephora. Non-compliance can result in fines, recalls, or damage to the brand’s reputation.
Concluding Analysis
Sephora has established itself as a leader in the beauty retail industry by offering a diverse range of products, exceptional customer service, and innovative shopping experiences. With its strong brand identity and extensive resources, Sephora is well-positioned to continue its growth and maintain its competitive edge in the dynamic beauty market. However, it must remain vigilant to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics to sustain its success in the long term.
Additional Resources
To keep learning and advancing your career, we highly recommend these additional resources:
Business Model Canvas of The Top 1,000 Largest Companies by Market Cap in 2024
A List of 1000 Venture Capital Firms & Investors with LinkedIn Profiles
Peter Thiel and the 16 Unicorns: The Legacy of Thiel Fellowship